|
Country Information |
Following
General Musharraf's decision to cooperate with the US-led
coalition against the Taliban regime and supporters of Osama
bin Laden in Afghanistan, the United States lifted bilateral
sanctions against Pakistan. Islamabad's withdrawal of support
for the Taliban regime cleared the way for a favourable
rescheduling of the country's external debt and provided
aid packages to assist with poverty alleviation and refugees.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has approved a US
$1.3 billion loan for Pakistan to help fight poverty and
offset the economic impact of the war in Afghanistan.
After
discussions between President Bush and Musharraf in February
2002, the White House announced its intention to work with
Congress to increase assistance to Pakistan, particularly
in areas related to debt relief, increased trade, education
reform and defence and security cooperation. Bush has agreed
to offer Pakistan up to US $1 billion in debt relief before
the end of 2003. Pakistan currently spends an estimated
80 percent of its annual budget on debt servicing. Islamabad
has the eighth largest army in the world - a major drain
on the national fiscus. The government justifies high spending
on the military by the need to counter Indian beligerence
in disputed Kashmir.
 Pakistan's
population of 145 million is increasing by 3-4 million people
per year - one of the fastest growth rates in the world.
This rapid growth is placing unprecedented pressure on the
country's social fabric and meagre natural resources. In
addition, the country hosts at least two million Afghan
refugees. The refugee population has severely strained Pakistan's
resources, including its healthcare system. Although political
changes in neighbouring Afghanistan mean many refugees will
return, UNHCR's prediction of mass migration in 2002 looks
unlikely until security and food availability improve throughout
the country. The ongoing dispute with India over Kashmir
has also created a sizeable refugee population. Pakistan's
population of 145 million is increasing by 3-4 million people
per year - one of the fastest growth rates in the world.
This rapid growth is placing unprecedented pressure on the
country's social fabric and meagre natural resources. In
addition, the country hosts at least two million Afghan
refugees. The refugee population has severely strained Pakistan's
resources, including its healthcare system. Although political
changes in neighbouring Afghanistan mean many refugees will
return, UNHCR's prediction of mass migration in 2002 looks
unlikely until security and food availability improve throughout
the country. The ongoing dispute with India over Kashmir
has also created a sizeable refugee population.
Largely
dependent on its agricultural output, Pakistan has suffered
the twin effects of a four-year drought and the lack of
an effective national water management strategy. Up to 350,000
people in the southwestern province of Baluchistan remain
dependant on international food aid, while an estimated
four million people in the southern port city of Karachi
do not have access to potable water. More than 70 percent
of the population are illiterate due to a lack of educational
services. Ethnic and sectarian tensions remain in major
cities, much of it fuelled by religious-based political
parties. Child labour is common throughout Pakistan, particularly
in the growing informal sector.
Fears
of rising drug consumption have grown in recent months because
an upsurge of supplies from Afghanistan have led to lower
prices. Despite Afghan government attempts to destroy the
spring crop, opium and heroin will be continue to be cheaply
available in Pakistani in 2002. HIV/AIDS infection rates
remain low in Pakistan, particularly in comparison to India,
Bangladesh and Nepal, but the disease will find its way
into the general population through the traditional transmission
routes unless the government launches a concerted education
and testing campaign to fight it.
Environmental
concerns include deforestation, soil erosion and desertification.
North ans western parts of the country are susceptible to
earthquakes, the latest in March 2002 caused considerable
damage in northwestern parts of the country. The river Indus
floods along its lower reaches during the monsoon.
Islamist
groups opposed to Pakistan's support for US action in Afghanistan
are becoming increasingly belligerent towards the government
and may prove to be a threat in the future. Western confidence
in Pakistan's ability to combat the terrorist threat was
shaken in March after a grenade attack on an Islamabad church
frequented by foreigners. Musharraf intends to remain in
power until 2007 and a referendum to legitimise this is
to be held in late April. However, his lack of a significant
political support base may lead to tension between the president
and parliament, due to be elected in October 2002.
Created
during the partition of the Indian sub-continent in 1947,
Pakistan has retained a long history of military rule. In
1977, Pakistan's elected prime minister, Zulfikar Ali Bhutto,
was overthrown by General Zia ul Haq who enforced martial
law and ruled until 1988. History was repeated when General
Musharraf overthrew prime minister Nawaz Sharif in a bloodless
coup on charges of corruption. General Musharraf dissolved
parliament and declared himself president in June 2001.
|
|
| Country
Data |
| Capital |
Islamabad |
|
|
| Population |
147 million |
|
|
| Life Expectancy |
61.82 |
|
|
| GDP |
$299 billion (purchasing power parity) |
|
|
| GDP per capita |
$2,100 (purchasing power parity) |
|
|
| Political structure |
Military
dictatorship. The main political parties in the country
are the Pakistan Muslim League (PML) and the Pakistan
People's Party (PPP). Other parties with a strong regional,
ethnic or religious base include the Awami National
Party (ANP), the Muttahida Qaumi Movement (MQM), and
the Jamaat-i-Islami (JI).
The
country is made up of four provinces, the Punjab, Sindh,
North West Frontier, and Balochistan, which come under
the authority of the governor and provincial cabinet,
appointed by the chief executive. The Northern Areas
and Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) are administered
by the federal government, but have considerable autonomy.
|
|
|
| Independence |
14 August, 1947 from India and the United Kingdom |
|
|
| Ethnic Groups |
Punjabi, Sindhi, Pashtun (Pathan), Baloch, Muhajir |
|
|
| Religions |
Muslim 97 percent (Sunni 77 percent, Shi'a 20 percent), Christian, Hindu, and other 3 percent |
|
|
| Geography |
Arid to semi arid plains, rugged mountains |
|
|
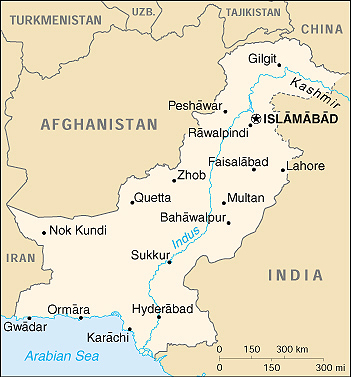
| Border countries |
India, Afghanistan, Iran and China |
|
|
| Natural resources |
Arable land, natural gas, limited petroleum, substantial hydro-electric potential, coal, iron ore, copper, salt, limestone |
|
|
| Agriculture products |
Wheat, cotton, rice, sugarcane, tobacco |
|
|
| Other products |
Textiles, fertiliser, steel products, chemicals, food processing,
oil and gas products, cement |
|
|
| Literacy rate |
55.3 percent (male)
29 percent (female) |
|
|
| Under five mortality rate |
78.52 (per 1,000 live births) |
|
|
| HIV/AIDS prevalence |
0.1 percent |
|
|
| External debt |
$31.5 billion (2001) |
|
|
| Economic aid |
$2 billion (fy1999/2000) |
|
|
| Internally displaced |
Not applicable |
|
|
| Refugees |
Pakistan is home to 2.5 million Afghan refugees, smaller minorities
include Iraqi's. |
|
|
Note: Pakistan ranked 142 on the UN Development Program's Human
Development Index for 2003.
Additional details
|
|
|
| Links
|
Links to other sources
US Committee for Refugees
US State Department
Background Notes
Pakistan News Service
|
|
Top
of the Page 
|
| ? |
|
View enlarged map
|